Willow Drop Format
Status: Proposal
 You really could transport Willow data using any of the means above.The Confidential Sync protocol presents a way for two peers with an established connection to efficiently exchange data. But running the necessary infrastructure to establish such connections (e.g. a STUN server, distributed hash table, or relay servers) is a non-trivial task, limiting who can operate them.
You really could transport Willow data using any of the means above.The Confidential Sync protocol presents a way for two peers with an established connection to efficiently exchange data. But running the necessary infrastructure to establish such connections (e.g. a STUN server, distributed hash table, or relay servers) is a non-trivial task, limiting who can operate them.
The Willow Drop Format presents a way for peers to transmit data to each other asynchronously and via completely user-improvised channels.
Instead of statefully coordinating which data to exchange, the Drop Format encodes drops, arbitrary sets of Entries and Payloads compiled into a single bytestring. A drop can then be treated as a kind of static set of stores which can be joined with any other stores as per the Willow Data Model.
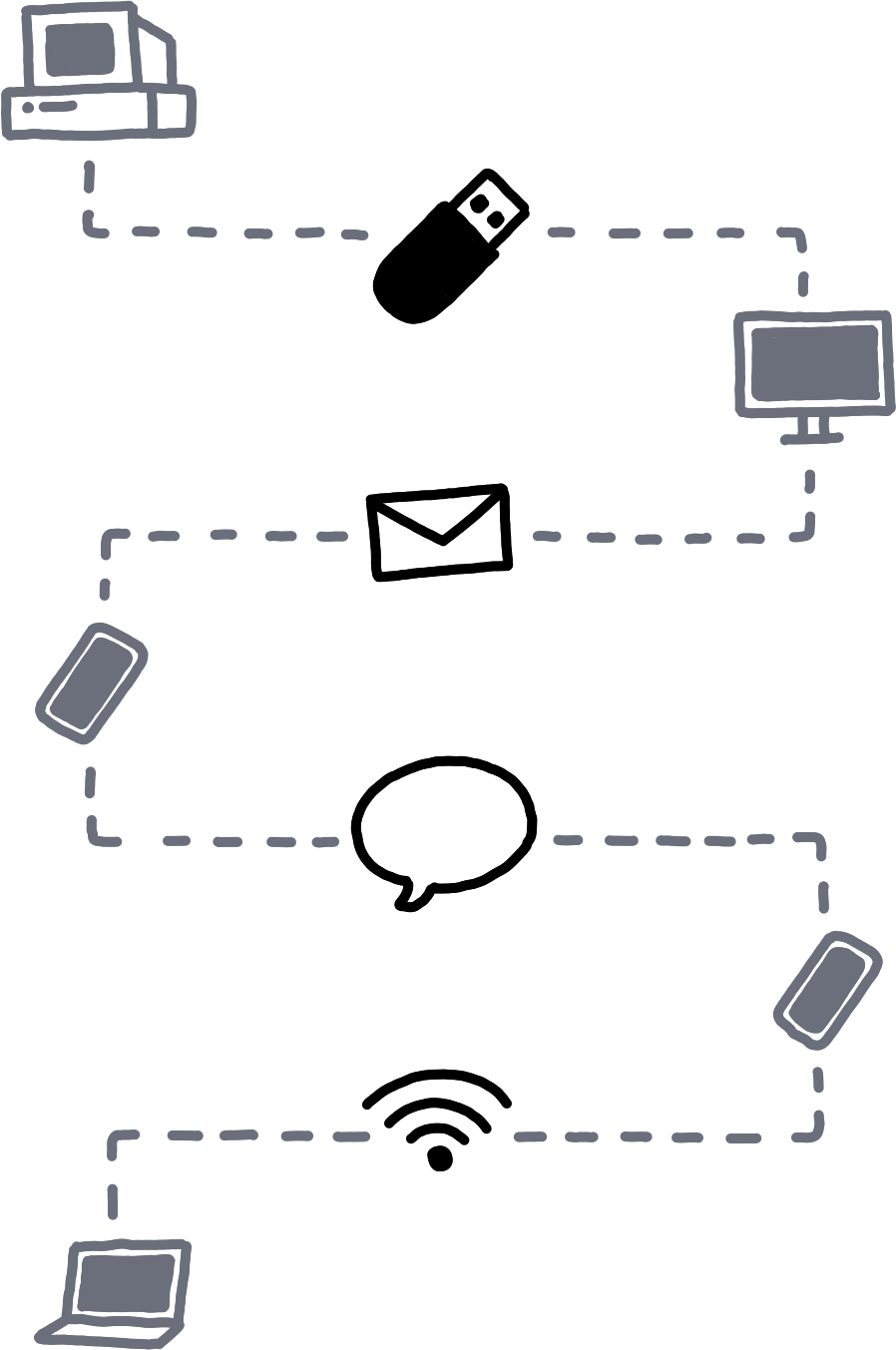 An example flow of Willow data travelling from device to device, first via USB key, then email, then a messaging app, then local wireless.Drops are then shared via informal ad-hoc infrastructure:
An example flow of Willow data travelling from device to device, first via USB key, then email, then a messaging app, then local wireless.Drops are then shared via informal ad-hoc infrastructure:
- USB keys
- SD cards
- CDs
- Email attachments
- Instant messages
- Torrents
- Or whatever means users have at hand.
Drops will often undoubtedly contain stale data that users are already aware of or no longer need. But what the Drop Format gives up in efficiency it more than makes up for in simplicity and flexibility. It is simple to implement, and works with the infrastructure users already have.
Parameters
See Drop Format Parameters for a default recommendation of parameters.In order to use the drop format, one must first specify a full suite of instantiations of the parameters of the core Willow data model. The hash_payload parameter of the data model must be a member of the Bab family of hash functions. In addition to this, the drop format requires the following:
- An encoding function encode_namespace_id for NamespaceId,
- An encoding function encode_subspace_id for SubspaceId,
- An encoding function encode_payload_digest for PayloadDigest,
- When using MeadowcapAuthorisationToken as the type of AuthorisationTokens, you can use EncodeMeadowcapAuthorisationTokenRelative.A relative encoding relation EncodeAuthorisationToken encoding AuthorisationTokens relative to pairs of an AuthorisedEntry (the previously encoded AuthorisedEntry) and an Entry (the Entry currently being encoded),
- a NamespaceId default_namespace_id,
- a SubspaceId default_subspace_id,
- a PayloadDigest default_payload_digest,
- an AuthorisationToken default_authorisation_token which authorises
default_entry(default_namespace_id, default_subspace_id, default_payload_digest), and
Format
A drop is a collection of entries, together with verifiable subslices of their payloads. The payload slice verification relies on Bab; drops store baseline verifiable slice streams of payload slices.
Let entries a sequence of pairs of a PossiblyAuthorisedEntries and a sequence of non-overlapping slices of payload chunks with stricly increasing start offsets. The Drop Format then defines how to encode this sequence as a single bytestring (the corresponding drop).
Let be the result of default_entry(default_namespace_id, default_subspace_id, default_payload_digest), and let be default_authorisation_token.
Then, the actual drop is the concatenation of the following:
| A tag of width for the length (number) of entries, followed by the corresponding compact U64 encoding. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For every -th pair ((, ), ) of entries , a concatenation of the following form:
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transport
Once created, a drop can be transported by whatever means a single bytestring can be transferred, so that the decoded entries can be ingested by its recipients.
We highly recommend encrypting drops for transport.
